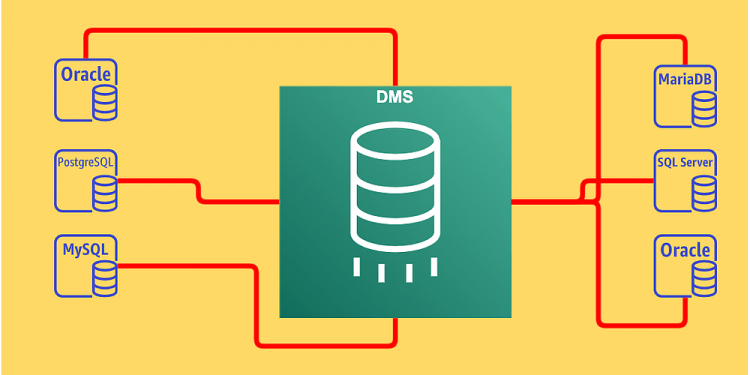
AWS DMS (Amazon Web Service Database Migration Service) is based in the cloud and enables quick and secure migration of databases to the Amazon Web Service. Users can migrate on-premises databases to the cloud, from one cloud provider to another, and even from the cloud to on-premises servers. The one critical condition for AWS DMS is that at least one of the databases, source or target, should be in the cloud.
During a migration with AWS DMS, the source database is fully functional and downtime is not required. This is a big advantage for large or mid-sized organizations for whom downtime for any length of time can be very inconvenient. Another advantage of AWS DMS is that databases can be migrated from the most common and open-source ones. Data can also be replicated continually with high availability and several databases can be consolidated into one petabyte-sized one by streaming data to Amazon Redshift or Amazon S3. Users get to use AWS DMS free for the first six months when databases are migrated to Amazon Redshift, Amazon DynamoDB, or Amazon Aurora.
Types of AWS DMS Database Migration
AWS DMS provides two types of database migration.
- Homogeneous database migration: In this form of database migration, both the database engines of the source and the target match each other. Examples of homogeneous migration are Microsoft SQL Server to Amazon RDS for SQL Server,MySQL to Amazon Aurora, Oracle to Amazon RDS for Oracle, or MySQL to Amazon RDS for MySQL. Due to the compatibility of the database engines, the migration is a simple one-step process as the schema structures, data types, and the data codes of the source and the target databases are similar.
AWS DMS migration can be stored with a click of a button as soon as the connection between the source and the target databases is established. The source database may be an Amazon RDS database or it can be based outside the AWS and running on an Amazon EC2 instance. The target database may be located in the Amazon EC2 instance or Amazon RDS.
- Heterogeneous database migration: As different from the previous types, the database engines here of the source and the target databases do not complement each other. Examples of heterogeneous migration include Oracle to Amazon Aurora, Microsoft SQL Server to MySQL migrations, or Oracle to PostgreSQL. A schema and code transformation have to be done before migration as the data types, schema structures, and the data codes of the source and the target are not the same.
Heterogeneous migration with AWS DMS is a two-step process. In the first step, the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) is used to convert the schema structure and the data code of the source database to match that of the target database. Only after this is the actual process of AWS DMS migration carried out. The conversion procedure is done automatically by AWS DMS. As in homogeneous migration, the source database can be on the Amazon RDS database that is located on-premises, offsite, or on an Amazon EC2 instance. The target database may be on Amazon EC2 or Amazon RDS.
Benefits of AWS DMS
Several aspects make AWS DMS a more optimized migration solution than the traditional processes.
- AWS DMS deploys, manages, and tracks all the infrastructure that is needed for migration. The migration process can be activated in minutes once the AWS DMS is configured. In comparison, traditional procedures were complex, necessitating the installation of new hardware and software and testing and debugging them.
- The cloud offers flexible storage capabilities. Data storage for migration is chargeable only for the volume of resources used. If additional resources are required, the same can be provided by AWS DMS in minutes and the migration resumed immediately. In contrast, the older licensing models charged flat upfront fees and often heavy maintenance charges.
- Automatic failover and reversal are critical features of AWS DMS. If an outage or a system failure occurs in the primary server, secondary servers in the region, on-premises, or in remote locations are immediately activated and take up the slack. When the outage is resolved, the failover acts in the reverse direction, the primary server is updated with incremental data, that is changes that have occurred in this outage period, and the migration carries on as before. There is no downtime or data loss because of the outage.
- AWS DMS automatically supports the infrastructure of the migration server including tracking the functioning of hardware and software, error reporting, and software patching.
- It is possible to change over to a more effective and optimized database engine than the one being used now. AWS DMS offers the benefit of managed database services from Amazon Relational Database Service or Amazon Aurora. Users can also migrate to fully managed data warehouse services like Amazon Redshift and NoSQL platforms like Amazon Dynamo DB, or affordable services like Amazon Simple Storage Service.
- AWS DMS supports the most popular DBMS engines as source databases. Similarly, several target database engines are supported by AWS DMS. Hence migration is possible between any supported source database to any supported target database.
- Finally, AWS DMS ensures that the migration procedure is very secure. Data at rest is completely encrypted with the AWS Key Management Service. On the other hand, the Secure Socket Layers (SSL) encrypts data in flight during migration from the source to the target database.
These are the reasons why AWS DMS is preferred for the migration of databases.
Follow Techdee for more!